Title: 前端进阶算法3:从浏览器缓存淘汰策略和Vue的keep-alive学习LRU算法 · Issue #9 · sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms · GitHub
Open Graph Title: 前端进阶算法3:从浏览器缓存淘汰策略和Vue的keep-alive学习LRU算法 · Issue #9 · sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms
X Title: 前端进阶算法3:从浏览器缓存淘汰策略和Vue的keep-alive学习LRU算法 · Issue #9 · sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms
Description: 引言 这个标题已经很明显的告诉我们:前端需要了解 LRU 算法! 这也是前端技能的亮点,当面试官在问到你前端开发中遇到过哪些算法,你也可以把这部分丢过去! 本节按以下步骤切入: 由浏览器缓存策略引出 LRU 算法原理 然后走进 vue 中 keep-alive 的应用 接着,透过 vue 中 keep-alive 源码看 LRU 算法的实现 最后,来一道 leetcode 题目,我们来实现一个 LRU 算法 按这个步骤来,完全掌握 LRU 算法,点亮前端技能,下面就开始...
Open Graph Description: 引言 这个标题已经很明显的告诉我们:前端需要了解 LRU 算法! 这也是前端技能的亮点,当面试官在问到你前端开发中遇到过哪些算法,你也可以把这部分丢过去! 本节按以下步骤切入: 由浏览器缓存策略引出 LRU 算法原理 然后走进 vue 中 keep-alive 的应用 接着,透过 vue 中 keep-alive 源码看 LRU 算法的实现 最后,来一道 leetcode 题目,我们来实现一...
X Description: 引言 这个标题已经很明显的告诉我们:前端需要了解 LRU 算法! 这也是前端技能的亮点,当面试官在问到你前端开发中遇到过哪些算法,你也可以把这部分丢过去! 本节按以下步骤切入: 由浏览器缓存策略引出 LRU 算法原理 然后走进 vue 中 keep-alive 的应用 接着,透过 vue 中 keep-alive 源码看 LRU 算法的实现 最后,来一道 leetcode 题目,我们来实现一...
Opengraph URL: https://github.com/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms/issues/9
X: @github
Domain: github.com
{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"DiscussionForumPosting","headline":"前端进阶算法3:从浏览器缓存淘汰策略和Vue的keep-alive学习LRU算法","articleBody":"\r\n\r\n### 引言\r\n\r\n这个标题已经很明显的告诉我们:前端需要了解 LRU 算法!\r\n\r\n这也是前端技能的亮点,当面试官在问到你前端开发中遇到过哪些算法,你也可以把这部分丢过去!\r\n\r\n本节按以下步骤切入:\r\n\r\n- 由浏览器缓存策略引出 LRU 算法原理\r\n- 然后走进 `vue` 中 `keep-alive` 的应用\r\n- 接着,透过 `vue` 中 `keep-alive` 源码看 `LRU` 算法的实现\r\n- 最后,来一道 leetcode 题目,我们来实现一个 LRU 算法\r\n\r\n按这个步骤来,完全掌握 LRU 算法,点亮前端技能,下面就开始吧👇\r\n\r\n### 一、LRU 缓存淘汰策略\r\n\r\n**缓存**在计算机网络上随处可见,例如:当我们首次访问一个网页时,打开很慢,但当我们再次打开这个网页时,打开就很快。\r\n\r\n这就涉及缓存在浏览器上的应用:**浏览器缓存**。当我们打开一个网页时,例如 `https://github.com/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms` ,它会在发起真正的网络请求前,查询浏览器缓存,看是否有要请求的文件,如果有,浏览器将会拦截请求,返回缓存文件,并直接结束请求,不会再去服务器上下载。如果不存在,才会去服务器请求。\r\n\r\n其实,浏览器中的缓存是一种在本地保存资源副本,它的大小是有限的,当我们请求数过多时,缓存空间会被用满,此时,继续进行网络请求就需要确定缓存中哪些数据被保留,哪些数据被移除,这就是**浏览器缓存淘汰策略**,最常见的淘汰策略有 FIFO(先进先出)、LFU(最少使用)、LRU(最近最少使用)。\r\n\r\nLRU ( `Least Recently Used` :最近最少使用 )缓存淘汰策略,故名思义,就是根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是 **如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高** ,优先淘汰最近没有被访问到的数据。\r\n\r\n画个图帮助我们理解:\r\n\r\n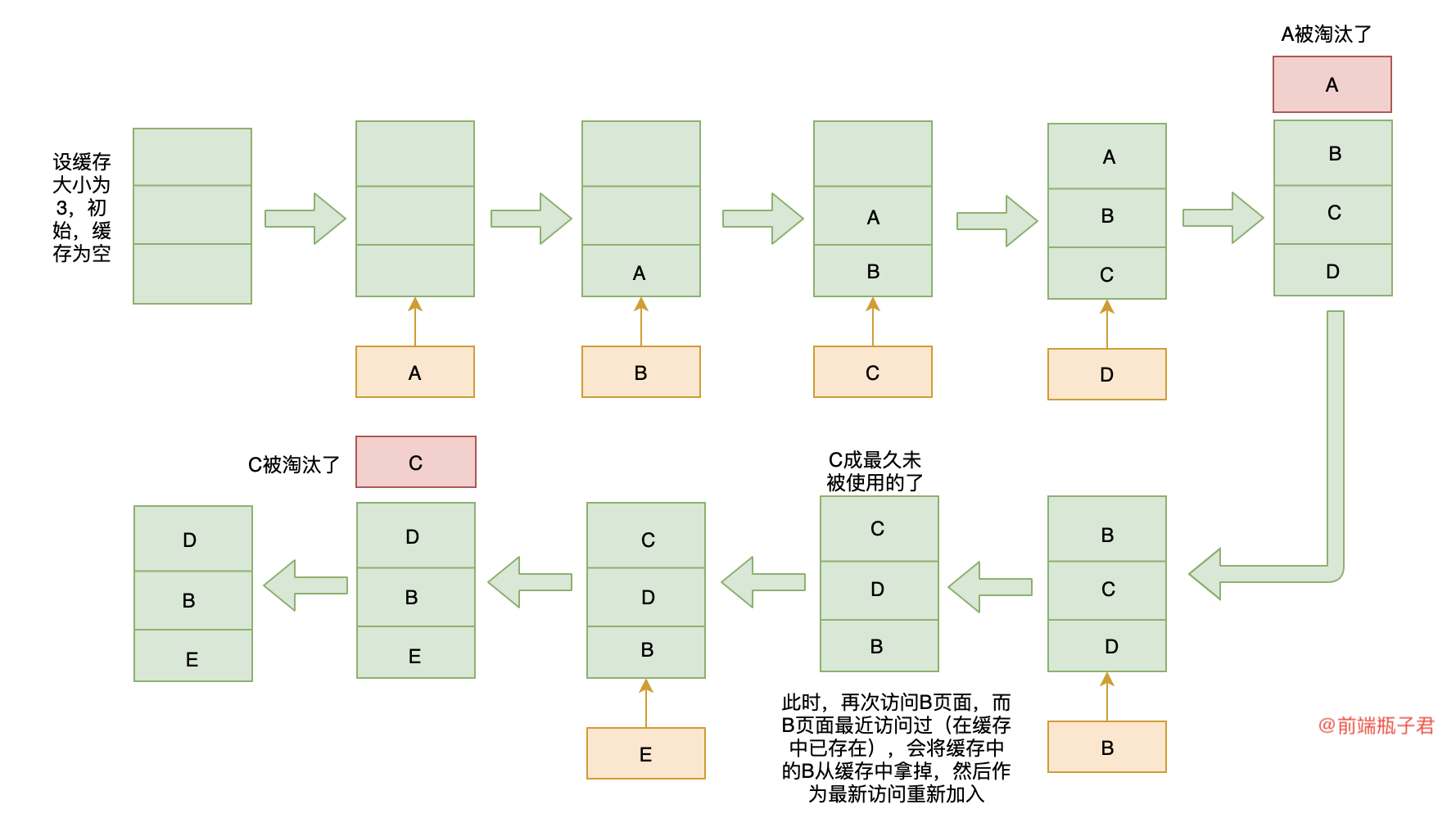\r\n\r\n\r\n\r\n### 二、LRU 在 keep-alive (Vue) 上的实现 \r\n\r\n#### 1. keep-alive \r\n\r\nkeep-alive 在 vue 中用于实现组件的缓存,当组件切换时不会对当前组件进行卸载。\r\n\r\n```vue\r\n\u003c!-- 基本 --\u003e\r\n\u003ckeep-alive\u003e\r\n \u003ccomponent :is=\"view\"\u003e\u003c/component\u003e\r\n\u003c/keep-alive\u003e\r\n```\r\n\r\n最常用的两个属性:`include` 、 `exculde` ,用于组件进行有条件的缓存,可以用逗号分隔字符串、正则表达式或一个数组来表示。\r\n\r\n在 2.5.0 版本中,`keep-alive` 新增了 `max` 属性,用于最多可以缓存多少组件实例,一旦这个数字达到了,在新实例被创建之前,已缓存组件中最久没有被访问的实例会被销毁掉,**看,这里就应用了 LRU 算法**。即在 `keep-alive` 中缓存达到 `max`,新增缓存实例会优先淘汰最近没有被访问到的实例🎉🎉🎉\r\n\r\n下面我们透过 vue 源码看一下具体的实现👇\r\n\r\n### 2. 从 vue 源码看 keep-alive 的实现\r\n\r\n```js\r\nexport default {\r\n name: \"keep-alive\",\r\n // 抽象组件属性 ,它在组件实例建立父子关系的时候会被忽略,发生在 initLifecycle 的过程中\r\n abstract: true, \r\n props: {\r\n // 被缓存组件\r\n include: patternTypes, \r\n // 不被缓存组件\r\n exclude: patternTypes,\r\n // 指定缓存大小\r\n max: [String, Number] \r\n },\r\n created() {\r\n // 初始化用于存储缓存的 cache 对象\r\n this.cache = Object.create(null);\r\n // 初始化用于存储VNode key值的 keys 数组\r\n this.keys = []; \r\n },\r\n destroyed() {\r\n for (const key in this.cache) {\r\n // 删除所有缓存\r\n pruneCacheEntry(this.cache, key, this.keys);\r\n }\r\n },\r\n mounted() {\r\n // 监听缓存(include)/不缓存(exclude)组件的变化\r\n // 在变化时,重新调整 cache\r\n // pruneCache:遍历 cache,如果缓存的节点名称与传入的规则没有匹配上的话,就把这个节点从缓存中移除\r\n this.$watch(\"include\", val =\u003e {\r\n pruneCache(this, name =\u003e matches(val, name));\r\n });\r\n this.$watch(\"exclude\", val =\u003e {\r\n pruneCache(this, name =\u003e !matches(val, name));\r\n });\r\n },\r\n render() {\r\n // 获取第一个子元素的 vnode\r\n const slot = this.$slots.default;\r\n const vnode: VNode = getFirstComponentChild(slot);\r\n const componentOptions: ?VNodeComponentOptions =\r\n vnode \u0026\u0026 vnode.componentOptions;\r\n if (componentOptions) {\r\n // name 不在 inlcude 中或者在 exlude 中则直接返回 vnode,否则继续进行下一步\r\n // check pattern\r\n const name: ?string = getComponentName(componentOptions);\r\n const { include, exclude } = this;\r\n if (\r\n // not included\r\n (include \u0026\u0026 (!name || !matches(include, name))) ||\r\n // excluded\r\n (exclude \u0026\u0026 name \u0026\u0026 matches(exclude, name))\r\n ) {\r\n return vnode;\r\n }\r\n \r\n const { cache, keys } = this;\r\n // 获取键,优先获取组件的 name 字段,否则是组件的 tag\r\n const key: ?string =\r\n vnode.key == null\r\n ? // same constructor may get registered as different local components\r\n // so cid alone is not enough (#3269)\r\n componentOptions.Ctor.cid +\r\n (componentOptions.tag ? `::${componentOptions.tag}` : \"\")\r\n : vnode.key;\r\n \r\n // --------------------------------------------------\r\n // 下面就是 LRU 算法了,\r\n // 如果在缓存里有则调整,\r\n // 没有则放入(长度超过 max,则淘汰最近没有访问的)\r\n // --------------------------------------------------\r\n // 如果命中缓存,则从缓存中获取 vnode 的组件实例,并且调整 key 的顺序放入 keys 数组的末尾\r\n if (cache[key]) {\r\n vnode.componentInstance = cache[key].componentInstance;\r\n // make current key freshest\r\n remove(keys, key);\r\n keys.push(key);\r\n }\r\n // 如果没有命中缓存,就把 vnode 放进缓存\r\n else {\r\n cache[key] = vnode;\r\n keys.push(key);\r\n // prune oldest entry\r\n // 如果配置了 max 并且缓存的长度超过了 this.max,还要从缓存中删除第一个\r\n if (this.max \u0026\u0026 keys.length \u003e parseInt(this.max)) {\r\n pruneCacheEntry(cache, keys[0], keys, this._vnode);\r\n }\r\n }\r\n \r\n // keepAlive标记位\r\n vnode.data.keepAlive = true;\r\n }\r\n return vnode || (slot \u0026\u0026 slot[0]);\r\n }\r\n};\r\n\r\n// 移除 key 缓存\r\nfunction pruneCacheEntry (\r\n cache: VNodeCache,\r\n key: string,\r\n keys: Array\u003cstring\u003e,\r\n current?: VNode\r\n) {\r\n const cached = cache[key]\r\n if (cached \u0026\u0026 (!current || cached.tag !== current.tag)) {\r\n cached.componentInstance.$destroy()\r\n }\r\n cache[key] = null\r\n remove(keys, key)\r\n}\r\n\r\n// remove 方法(shared/util.js)\r\n/**\r\n * Remove an item from an array.\r\n */\r\nexport function remove (arr: Array\u003cany\u003e, item: any): Array\u003cany\u003e | void {\r\n if (arr.length) {\r\n const index = arr.indexOf(item)\r\n if (index \u003e -1) {\r\n return arr.splice(index, 1)\r\n }\r\n }\r\n}\r\n```\r\n\r\n[keep-alive源码路径](https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/dev/src/core/components/keep-alive.js)\r\n\r\n在 `keep-alive` 缓存超过 `max` 时,使用的缓存淘汰算法就是 LRU 算法,它在实现的过程中用到了 `cache` 对象用于保存缓存的组件实例及 `key` 值,`keys` 数组用于保存缓存组件的 `key` ,当 `keep-alive` 中渲染一个需要缓存的实例时:\r\n\r\n- 判断缓存中是否已缓存了该实例,缓存了则直接获取,并调整 `key` 在 `keys` 中的位置(移除 `keys` 中 `key` ,并放入 `keys` 数组的最后一位)\r\n- 如果没有缓存,则缓存该实例,若 `keys` 的长度大于 `max` (缓存长度超过上限),则移除 `keys[0]` 缓存\r\n\r\n下面我们来自己实现一个 LRU 算法吧⛽️⛽️⛽️\r\n\r\n### 三、leetcode:LRU 缓存机制\r\n\r\n运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 `get` 和写入数据 `put` 。\r\n\r\n获取数据 `get(key)` - 如果密钥 ( `key` ) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 `-1` 。\r\n写入数据 `put(key, value)` - 如果密钥不存在,则写入数据。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据,从而为新数据留出空间。\r\n\r\n**进阶:**\r\n\r\n你是否可以在 **O(1)** 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?\r\n\r\n**示例:**\r\n\r\n```js\r\nLRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );\r\n\r\ncache.put(1, 1);\r\ncache.put(2, 2);\r\ncache.get(1); // 返回 1\r\ncache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得密钥 2 作废\r\ncache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)\r\ncache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得密钥 1 作废\r\ncache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)\r\ncache.get(3); // 返回 3\r\ncache.get(4); // 返回 4\r\n```\r\n\r\n前面已经介绍过了 `keep-alive` 中LRU实现源码,现在来看这道题是不是很简单😊😊😊,可以尝试自己解答一下⛽️,然后思考一下有没有什么继续优化的!欢迎提供更多的解法\r\n\r\n答案已提交到 https://github.com/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms/issues/7 \r\n\r\n### 四、认识更多的前端道友,一起进阶前端开发\r\n\r\n前端算法集训营第一期免费开营啦🎉🎉🎉,免费哟!\r\n\r\n在这里,你可以和志同道合的前端朋友们(600+)一起进阶前端算法,从0到1构建完整的数据结构与算法体系。\r\n\r\n在这里,瓶子君不仅介绍算法,还将算法与前端各个领域进行结合,包括浏览器、HTTP、V8、React、Vue源码等。\r\n\r\n在这里,你可以每天学习一道大厂算法题(阿里、腾讯、百度、字节等等)或 leetcode,瓶子君都会在第二天解答哟!\r\n\r\n更多福利等你解锁🔓🔓🔓!\r\n\r\n在公众号「前端瓶子君」内回复「算法」即可加入。你的关注就是对瓶子君最大的支持😄😄😄\r\n\r\n","author":{"url":"https://github.com/sisterAn","@type":"Person","name":"sisterAn"},"datePublished":"2020-04-07T01:32:54.000Z","interactionStatistic":{"@type":"InteractionCounter","interactionType":"https://schema.org/CommentAction","userInteractionCount":6},"url":"https://github.com/9/JavaScript-Algorithms/issues/9"}| route-pattern | /_view_fragments/issues/show/:user_id/:repository/:id/issue_layout(.:format) |
| route-controller | voltron_issues_fragments |
| route-action | issue_layout |
| fetch-nonce | v2:0387ba60-2205-adab-e95b-0b0f744527ad |
| current-catalog-service-hash | 81bb79d38c15960b92d99bca9288a9108c7a47b18f2423d0f6438c5b7bcd2114 |
| request-id | 8480:E7954:CCA43:11F323:696A6885 |
| html-safe-nonce | 9f73f92cb814d6ce34252052b2c46ecf8a804452362493ba110add5b6ce76e83 |
| visitor-payload | eyJyZWZlcnJlciI6IiIsInJlcXVlc3RfaWQiOiI4NDgwOkU3OTU0OkNDQTQzOjExRjMyMzo2OTZBNjg4NSIsInZpc2l0b3JfaWQiOiI3NTIxODc1NTE0MDEyMzYyODg1IiwicmVnaW9uX2VkZ2UiOiJpYWQiLCJyZWdpb25fcmVuZGVyIjoiaWFkIn0= |
| visitor-hmac | d027a47b94bff0cde6da10680d21ac81e50c71770443c736b815d245cc5d4b24 |
| hovercard-subject-tag | issue:595528785 |
| github-keyboard-shortcuts | repository,issues,copilot |
| google-site-verification | Apib7-x98H0j5cPqHWwSMm6dNU4GmODRoqxLiDzdx9I |
| octolytics-url | https://collector.github.com/github/collect |
| analytics-location | / |
| fb:app_id | 1401488693436528 |
| apple-itunes-app | app-id=1477376905, app-argument=https://github.com/_view_fragments/issues/show/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms/9/issue_layout |
| twitter:image | https://opengraph.githubassets.com/5ff14357c63e40de48a58c94d55e8880651b7b9237d558fac628e29a668759c0/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms/issues/9 |
| twitter:card | summary_large_image |
| og:image | https://opengraph.githubassets.com/5ff14357c63e40de48a58c94d55e8880651b7b9237d558fac628e29a668759c0/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms/issues/9 |
| og:image:alt | 引言 这个标题已经很明显的告诉我们:前端需要了解 LRU 算法! 这也是前端技能的亮点,当面试官在问到你前端开发中遇到过哪些算法,你也可以把这部分丢过去! 本节按以下步骤切入: 由浏览器缓存策略引出 LRU 算法原理 然后走进 vue 中 keep-alive 的应用 接着,透过 vue 中 keep-alive 源码看 LRU 算法的实现 最后,来一道 leetcode 题目,我们来实现一... |
| og:image:width | 1200 |
| og:image:height | 600 |
| og:site_name | GitHub |
| og:type | object |
| og:author:username | sisterAn |
| hostname | github.com |
| expected-hostname | github.com |
| None | 6fea32d5b7276b841b7a803796d9715bc6cfb31ed549fdf9de2948ac25d12ba6 |
| turbo-cache-control | no-preview |
| go-import | github.com/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms git https://github.com/sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms.git |
| octolytics-dimension-user_id | 19721451 |
| octolytics-dimension-user_login | sisterAn |
| octolytics-dimension-repository_id | 252061924 |
| octolytics-dimension-repository_nwo | sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms |
| octolytics-dimension-repository_public | true |
| octolytics-dimension-repository_is_fork | false |
| octolytics-dimension-repository_network_root_id | 252061924 |
| octolytics-dimension-repository_network_root_nwo | sisterAn/JavaScript-Algorithms |
| turbo-body-classes | logged-out env-production page-responsive |
| disable-turbo | false |
| browser-stats-url | https://api.github.com/_private/browser/stats |
| browser-errors-url | https://api.github.com/_private/browser/errors |
| release | f2d9f6432a5a115ec709295ae70623f33bb80aee |
| ui-target | full |
| theme-color | #1e2327 |
| color-scheme | light dark |
Links:
Viewport: width=device-width